Lightning in 2 steps¶
In this guide we’ll show you how to organize your PyTorch code into Lightning in 2 steps.
Organizing your code with PyTorch Lightning makes your code:
Keep all the flexibility (this is all pure PyTorch), but removes a ton of boilerplate
More readable by decoupling the research code from the engineering
Easier to reproduce
Less error-prone by automating most of the training loop and tricky engineering
Scalable to any hardware without changing your model
Here’s a 3 minute conversion guide for PyTorch projects:
Step 0: Install PyTorch Lightning¶
You can install using pip
pip install pytorch-lightning
Or with conda (see how to install conda here):
conda install pytorch-lightning -c conda-forge
You could also use conda environments
conda activate my_env
pip install pytorch-lightning
Import the following:
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, random_split
import pytorch_lightning as pl
Step 1: Define LightningModule¶
class LitAutoEncoder(pl.LightningModule):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(28 * 28, 64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(64, 3))
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(3, 64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(64, 28 * 28))
def forward(self, x):
# in lightning, forward defines the prediction/inference actions
embedding = self.encoder(x)
return embedding
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# training_step defined the train loop.
# It is independent of forward
x, y = batch
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
z = self.encoder(x)
x_hat = self.decoder(z)
loss = F.mse_loss(x_hat, x)
# Logging to TensorBoard by default
self.log("train_loss", loss)
return loss
def configure_optimizers(self):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
return optimizer
SYSTEM VS MODEL
A lightning module defines a system not a model.
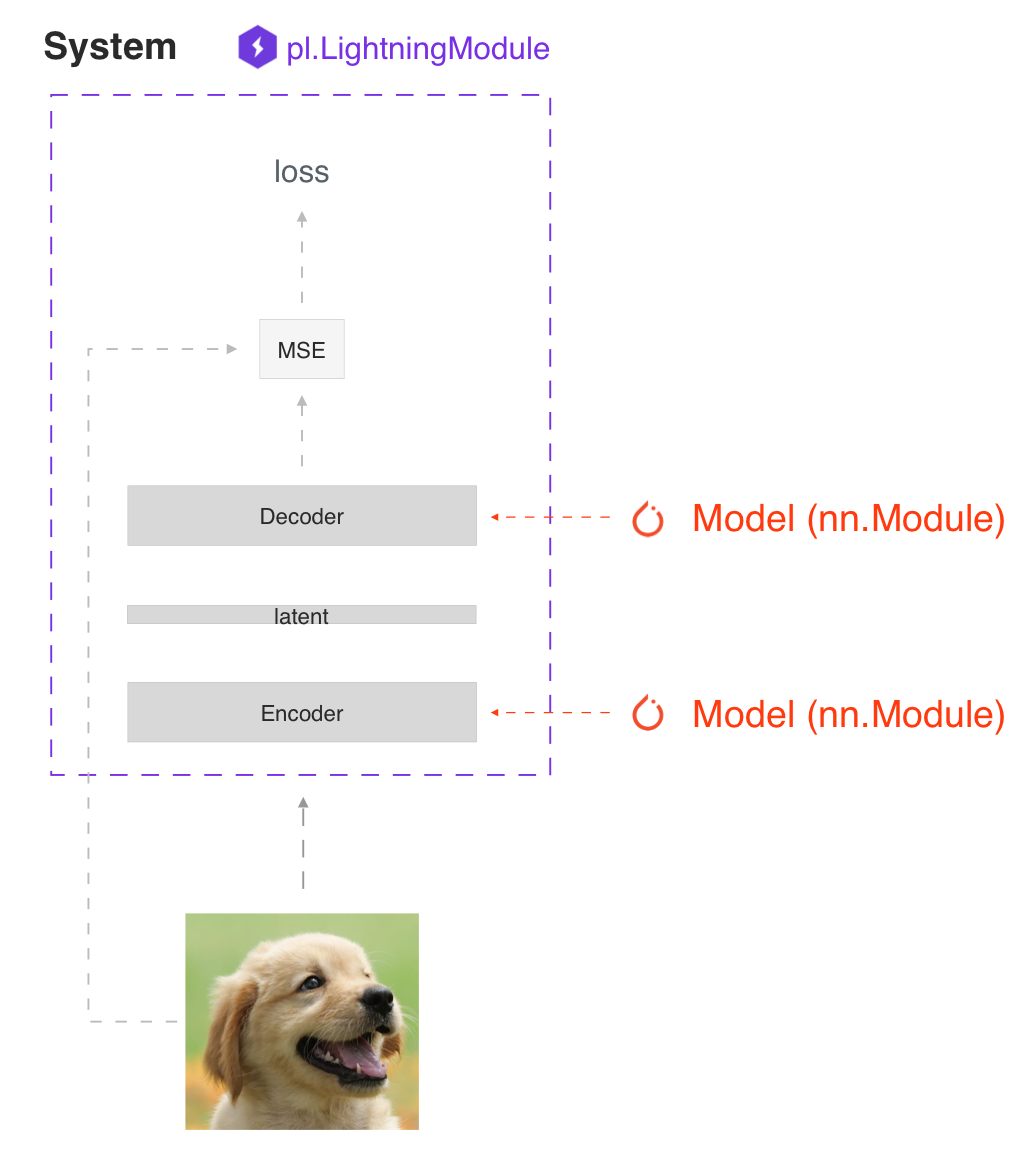
Examples of systems are:
Seq2seq
Under the hood a LightningModule is still just a torch.nn.Module that groups all research code into a single file to make it self-contained:
The Train loop
The Validation loop
The Test loop
The Prediction loop
The Model or system of Models
The Optimizer
You can customize any part of training (such as the backward pass) by overriding any of the 20+ hooks found in Available Callback hooks
class LitAutoEncoder(LightningModule):
def backward(self, loss, optimizer, optimizer_idx):
loss.backward()
FORWARD vs TRAINING_STEP
In Lightning we separate training from inference. The training_step defines the full training loop. We encourage users to use the forward to define inference actions.
For example, in this case we could define the autoencoder to act as an embedding extractor:
def forward(self, x):
embeddings = self.encoder(x)
return embeddings
Of course, nothing is stopping you from using forward from within the training_step.
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
...
z = self(x)
It really comes down to your application. We do, however, recommend that you keep both intents separate.
Use forward for inference (predicting).
Use training_step for training.
More details in lightning module docs.
Step 2: Fit with Lightning Trainer¶
First, define the data however you want. Lightning just needs a DataLoader for the train/val/test/predict splits.
dataset = MNIST(os.getcwd(), download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset)
Next, init the lightning module and the PyTorch Lightning Trainer,
then call fit with both the data and model.
# init model
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
# most basic trainer, uses good defaults (auto-tensorboard, checkpoints, logs, and more)
# trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=8) (if you have GPUs)
trainer = pl.Trainer()
trainer.fit(autoencoder, train_loader)
The Trainer automates:
Epoch and batch iteration
Calling of optimizer.step(), backward, zero_grad()
Calling of .eval(), enabling/disabling grads
Tensorboard (see loggers options)
Multi-GPU support
16-bit precision AMP support
Tip
If you prefer to manually manage optimizers you can use the Manual optimization mode (ie: RL, GANs, etc…).
That’s it!
These are the main 2 concepts you need to know in Lightning. All the other features of lightning are either features of the Trainer or LightningModule.
Basic features¶
Manual vs automatic optimization¶
Automatic optimization¶
With Lightning, you don’t need to worry about when to enable/disable grads, do a backward pass, or update optimizers as long as you return a loss with an attached graph from the training_step, Lightning will automate the optimization.
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
loss = self.encoder(batch)
return loss
Manual optimization¶
However, for certain research like GANs, reinforcement learning, or something with multiple optimizers or an inner loop, you can turn off automatic optimization and fully control the training loop yourself.
Turn off automatic optimization and you control the train loop!
def __init__(self):
self.automatic_optimization = False
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# access your optimizers with use_pl_optimizer=False. Default is True,
# setting use_pl_optimizer=True will maintain plugin/precision support
opt_a, opt_b = self.optimizers(use_pl_optimizer=True)
loss_a = self.generator(batch)
opt_a.zero_grad()
# use `manual_backward()` instead of `loss.backward` to automate half precision, etc...
self.manual_backward(loss_a)
opt_a.step()
loss_b = self.discriminator(batch)
opt_b.zero_grad()
self.manual_backward(loss_b)
opt_b.step()
Loop customization¶
If you need even more flexibility, you can fully customize the training loop to its core. Learn more about loops here.
Predict or Deploy¶
When you’re done training, you have 3 options to use your LightningModule for predictions.
Option 1: Sub-models¶
Pull out any model inside your system for predictions.
# ----------------------------------
# to use as embedding extractor
# ----------------------------------
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder.load_from_checkpoint("path/to/checkpoint_file.ckpt")
encoder_model = autoencoder.encoder
encoder_model.eval()
# ----------------------------------
# to use as image generator
# ----------------------------------
decoder_model = autoencoder.decoder
decoder_model.eval()
Option 2: Forward¶
You can also add a forward method to do predictions however you want.
# ----------------------------------
# using the AE to extract embeddings
# ----------------------------------
class LitAutoEncoder(LightningModule):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential()
def forward(self, x):
embedding = self.encoder(x)
return embedding
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
embedding = autoencoder(torch.rand(1, 28 * 28))
# ----------------------------------
# or using the AE to generate images
# ----------------------------------
class LitAutoEncoder(LightningModule):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.decoder = nn.Sequential()
def forward(self):
z = torch.rand(1, 3)
image = self.decoder(z)
image = image.view(1, 1, 28, 28)
return image
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
image_sample = autoencoder()
Option 3: Production¶
For production systems, onnx or torchscript are much faster. Make sure you have added a forward method or trace only the sub-models you need.
# ----------------------------------
# torchscript
# ----------------------------------
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
torch.jit.save(autoencoder.to_torchscript(), "model.pt")
os.path.isfile("model.pt")
# ----------------------------------
# onnx
# ----------------------------------
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx", delete=False) as tmpfile:
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
input_sample = torch.randn((1, 28 * 28))
autoencoder.to_onnx(tmpfile.name, input_sample, export_params=True)
os.path.isfile(tmpfile.name)
Using CPUs/GPUs/TPUs/IPUs¶
It’s trivial to use CPUs, GPUs, TPUs or IPUs in Lightning. There’s NO NEED to change your code, simply change the Trainer options.
# train on CPU
trainer = Trainer()
# train on 8 CPUs
trainer = Trainer(num_processes=8)
# train on 1024 CPUs across 128 machines
trainer = pl.Trainer(num_processes=8, num_nodes=128)
# train on 1 GPU
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=1)
# train on multiple GPUs across nodes (32 gpus here)
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=4, num_nodes=8)
# train on gpu 1, 3, 5 (3 gpus total)
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=[1, 3, 5])
# Multi GPU with mixed precision
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=2, precision=16)
# Train on TPUs
trainer = pl.Trainer(tpu_cores=8)
Without changing a SINGLE line of your code, you can now do the following with the above code:
# train on TPUs using 16 bit precision
# using only half the training data and checking validation every quarter of a training epoch
trainer = pl.Trainer(tpu_cores=8, precision=16, limit_train_batches=0.5, val_check_interval=0.25)
# Train on IPUs
trainer = pl.Trainer(ipus=8)
Checkpoints¶
Lightning automatically saves your model. Once you’ve trained, you can load the checkpoints as follows:
model = LitModel.load_from_checkpoint(path)
The above checkpoint contains all the arguments needed to init the model and set the state dict. If you prefer to do it manually, here’s the equivalent
# load the ckpt
ckpt = torch.load("path/to/checkpoint.ckpt")
# equivalent to the above
model = LitModel()
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["state_dict"])
Data flow¶
Each loop (training, validation, test, predict) has three hooks you can implement:
x_step
x_step_end
x_epoch_end
To illustrate how data flows, we’ll use the training loop (ie: x=training)
outs = []
for batch in data:
out = training_step(batch)
outs.append(out)
training_epoch_end(outs)
The equivalent in Lightning is:
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
prediction = ...
return prediction
def training_epoch_end(self, outs):
for out in outs:
...
In the event that you use DP or DDP2 distributed modes (ie: split a batch across GPUs), use the x_step_end to manually aggregate (or don’t implement it to let lightning auto-aggregate for you).
for batch in data:
model_copies = copy_model_per_gpu(model, num_gpus)
batch_split = split_batch_per_gpu(batch, num_gpus)
gpu_outs = []
for model, batch_part in zip(model_copies, batch_split):
# LightningModule hook
gpu_out = model.training_step(batch_part)
gpu_outs.append(gpu_out)
# LightningModule hook
out = training_step_end(gpu_outs)
The lightning equivalent is:
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
loss = ...
return loss
def training_step_end(self, losses):
gpu_0_loss = losses[0]
gpu_1_loss = losses[1]
return (gpu_0_loss + gpu_1_loss) / 2
Tip
The validation, test and prediction loops have the same structure.
Logging¶
To log to Tensorboard, your favorite logger, and/or the progress bar, use the
log() method which can be called from
any method in the LightningModule.
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
self.log("my_metric", x)
The log() method has a few options:
on_step (logs the metric at that step in training)
on_epoch (automatically accumulates and logs at the end of the epoch)
prog_bar (logs to the progress bar)
logger (logs to the logger like Tensorboard)
Depending on where the log is called from, Lightning auto-determines the correct mode for you. But of course you can override the default behavior by manually setting the flags
Note
Setting on_epoch=True will accumulate your logged values over the full training epoch.
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
self.log("my_loss", loss, on_step=True, on_epoch=True, prog_bar=True, logger=True)
Note
The loss value shown in the progress bar is smoothed (averaged) over the last values, so it differs from the actual loss returned in the train/validation step.
You can also use any method of your logger directly:
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
tensorboard = self.logger.experiment
tensorboard.any_summary_writer_method_you_want()
Once your training starts, you can view the logs by using your favorite logger or booting up the Tensorboard logs:
tensorboard --logdir ./lightning_logs
Note
Lightning automatically shows the loss value returned from training_step in the progress bar.
So, no need to explicitly log like this self.log('loss', loss, prog_bar=True).
Read more about loggers.
Optional extensions¶
Callbacks¶
A callback is an arbitrary self-contained program that can be executed at arbitrary parts of the training loop.
Here’s an example adding a not-so-fancy learning rate decay rule:
from pytorch_lightning.callbacks import Callback
class DecayLearningRate(Callback):
def __init__(self):
self.old_lrs = []
def on_train_start(self, trainer, pl_module):
# track the initial learning rates
for opt_idx, optimizer in enumerate(trainer.optimizers):
group = [param_group["lr"] for param_group in optimizer.param_groups]
self.old_lrs.append(group)
def on_train_epoch_end(self, trainer, pl_module):
for opt_idx, optimizer in enumerate(trainer.optimizers):
old_lr_group = self.old_lrs[opt_idx]
new_lr_group = []
for p_idx, param_group in enumerate(optimizer.param_groups):
old_lr = old_lr_group[p_idx]
new_lr = old_lr * 0.98
new_lr_group.append(new_lr)
param_group["lr"] = new_lr
self.old_lrs[opt_idx] = new_lr_group
# And pass the callback to the Trainer
decay_callback = DecayLearningRate()
trainer = Trainer(callbacks=[decay_callback])
Things you can do with a callback:
Send emails at some point in training
Grow the model
Update learning rates
Visualize gradients
…
You are only limited by your imagination
LightningDataModules¶
DataLoaders and data processing code tends to end up scattered around.
Make your data code reusable by organizing it into a LightningDataModule.
class MNISTDataModule(LightningDataModule):
def __init__(self, batch_size=32):
super().__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
# When doing distributed training, Datamodules have two optional arguments for
# granular control over download/prepare/splitting data:
# OPTIONAL, called only on 1 GPU/machine
def prepare_data(self):
MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True, download=True)
MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False, download=True)
# OPTIONAL, called for every GPU/machine (assigning state is OK)
def setup(self, stage: Optional[str] = None):
# transforms
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])
# split dataset
if stage in (None, "fit"):
mnist_train = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True, transform=transform)
self.mnist_train, self.mnist_val = random_split(mnist_train, [55000, 5000])
if stage == "test":
self.mnist_test = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False, transform=transform)
if stage == "predict":
self.mnist_predict = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False, transform=transform)
# return the dataloader for each split
def train_dataloader(self):
mnist_train = DataLoader(self.mnist_train, batch_size=self.batch_size)
return mnist_train
def val_dataloader(self):
mnist_val = DataLoader(self.mnist_val, batch_size=self.batch_size)
return mnist_val
def test_dataloader(self):
mnist_test = DataLoader(self.mnist_test, batch_size=self.batch_size)
return mnist_test
def predict_dataloader(self):
mnist_predict = DataLoader(self.mnist_predict, batch_size=self.batch_size)
return mnist_predict
LightningDataModule is designed to enable sharing and reusing data splits
and transforms across different projects. It encapsulates all the steps needed to process data: downloading,
tokenizing, processing etc.
Now you can simply pass your LightningDataModule to
the Trainer:
# init model
model = LitModel()
# init data
dm = MNISTDataModule()
# train
trainer = pl.Trainer()
trainer.fit(model, datamodule=dm)
# validate
trainer.validate(datamodule=dm)
# test
trainer.test(datamodule=dm)
# predict
predictions = trainer.predict(datamodule=dm)
DataModules are specifically useful for building models based on data. Read more on datamodules.
Debugging¶
Lightning has many tools for debugging. Here is an example of just a few of them:
# use only 10 train batches and 3 val batches
trainer = Trainer(limit_train_batches=10, limit_val_batches=3)
# Automatically overfit the same batch of your model for a sanity test
trainer = Trainer(overfit_batches=1)
# unit test all the code - hits every line of your code once to see if you have bugs,
# instead of waiting hours to crash on validation
trainer = Trainer(fast_dev_run=True)
# unit test all the code - hits every line of your code with 4 batches
trainer = Trainer(fast_dev_run=4)
# train only 20% of an epoch
trainer = Trainer(limit_train_batches=0.2)
# run validation every 25% of a training epoch
trainer = Trainer(val_check_interval=0.25)
# Profile your code to find speed/memory bottlenecks
Trainer(profiler="simple")
Other cool features¶
Once you define and train your first Lightning model, you might want to try other cool features like
Or read our Guide to learn more!
Grid AI¶
Grid AI is our native solution for large scale training and tuning on the cloud.
Get started for free with your GitHub or Google Account here.
Community¶
Our community of core maintainers and thousands of expert researchers is active on our Slack and GitHub Discussions. Drop by to hang out, ask Lightning questions or even discuss research!
Masterclass¶
We also offer a Masterclass to teach you the advanced uses of Lightning.

